Finding Serialization PHP Gadget chain
TL;DR
In this article, you will find an introduction to vulnerabilities related to insecure serialization and the solution to the ‘Unserial killer’ challenge of the DG’hAck 2022.
More specifically, we will talk about attribute/object injections and gadget chain research in PHP libraries.
Insecure deserialization
In this section, we will make an introduction to insecure deserialization vulnerabilities. If you are already familiar with this kind of vulnerability, you can skip this section.
Serialization
Serialization is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored or transmitted and reconstructed later
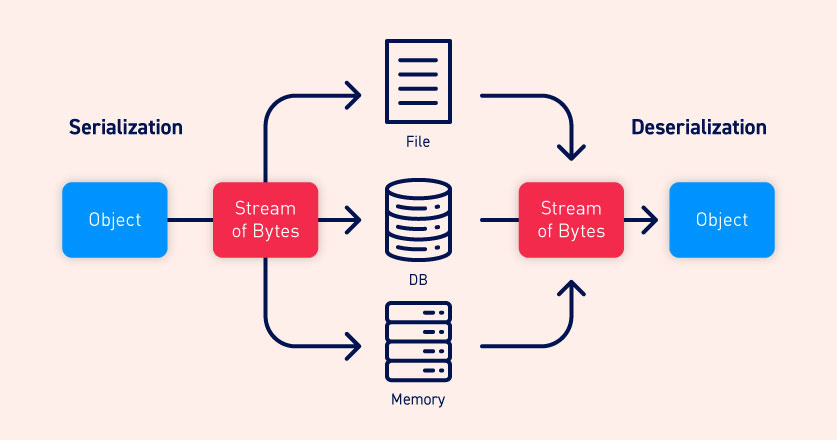
Image source, PortSwigger - Insecure deserialization.
In PHP, you have two functions to deal with serialization.
- serialize - Generates a storable representation of a value.
- unserialize - Creates a PHP value from a stored representation.
Attribute injection
Attribute injection is a kind of deserialization vulnerability when an attacker has the possibility to change the value of an instance’s attribute.
To demonstrate this kind of vulnerability, we will use a basic class with only two attributes :
|
|
The instance $user of the class User can be represented as a string using serialization:
|
|
If an attacker can control the input of the unserialize function, it can, for example, edit the isAdmin instance’s attribute and set it to true. Later on, this may lead to access control issues.
|
|
By changing the value from 0 to 1, the isAdmin attribute is now set to true:
|
|
Object injection
Instead of modifying the attributes of the User object. It is possible to unserialize an instance of another object. This can potentially allow code execution, file writing or reading, calling a protected function, …
To do this, we can use PHP gadgets inside the application code or inside the PHP libraries. A gadget is a piece of code that allows an attacker to achieve a particular goal.
In order to execute one or multiple gadgets (PHP code) from a serialization, we can use the power of PHP magic methods. Magic methods are special methods which override PHP’s default’s action when certain actions are performed on an object.
Examples of interesting magic methods:
- __wakeup() : invoked on unserialize()
- __destruct() : invoked on garbage collection (no references to the instance)
- __toString() : invoked when the object is treated as a string
- __call() : invoked when an undefined method is called
- __construct() : invoked on each newly-created object
- …
Imagine that your project contains a PHP library that has the following class :
|
|
The unlink PHP function deletes the file passed as parameter.
If your application is vulnerable to insecure deserialization, an attacker could delete any file on the system as long as the process has the permission to delete it. Why? Because the __destruct magic method will be automatically called when the instance will be removed by the garbage collector. Indeed, you just need to set the value of the filePath attribute to the file you want to delete.
Here is an example that will delete the file at /tmp/toto :
|
|
An instance of FileManager will be created by the unserialize function and then automatically deleted by the garbage collector. Afterwards, the __dectruct function will be called and the file will be deleted :
|
|
Generic Gadget chain
So researchers started looking for gadgets in known PHP libraries like Symfony, Laravel, ZendFramework, … This will allow an attacker to exploit a PHP application that has an insecure unserialization vulnerability and a library with known gadgets.
A list of gadgets in known PHP libraries is available on this Github repository : PHPGGC: PHP Generic Gadget Chains
Unserial killer - Writeup
Introduction
Unserial killer is a challenge of the DG’hAck 2022 edition. This challenge belongs to the web category. The difficulty of the challenge is rated as hard and has been solved 19 times out of 945 participants.
Description : A company has just been attacked by hackers who have taken over the configuration of one of their web servers. Audit the web server’s source code and find out how they gained access to it. http://unserialkiller2.chall.malicecyber.com/
Each section of the writeup has a summary at the end. This allows you to check that you understand the solution thread.
Goal of the challenge
The web application provides us with its source code and tells us that the configuration of the application is present in the config.php.
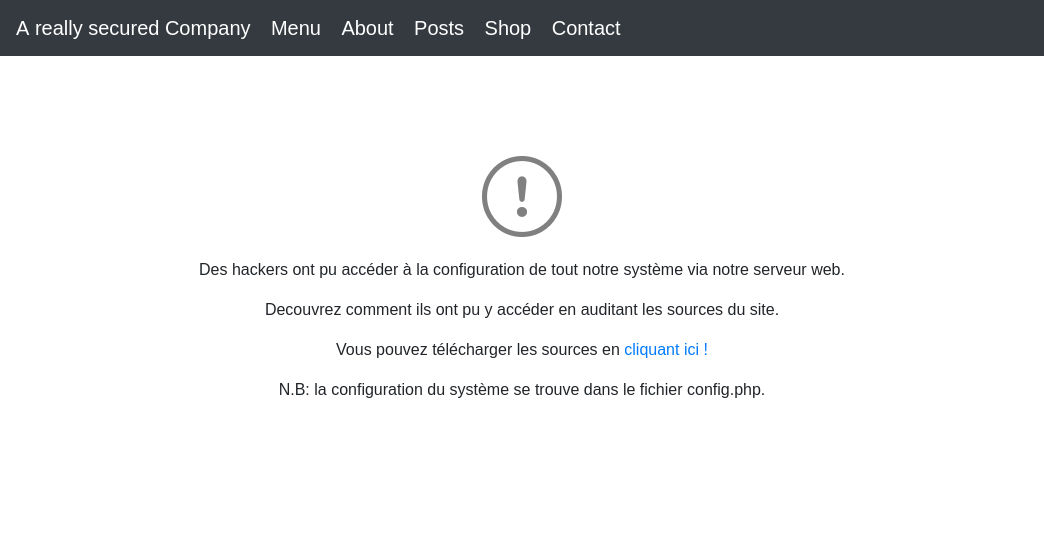
The source code of the PHP application is very minimalist, it contains only :
- Some HTML
- A function that allows us to unserialize data sent by the user
- Few PHP libraries (in the
vendorfolder)
We also learn that the flag is in the configuration file, so the goal is to read the config.php file at the web root. Here is the interesting part of the application code:
|
|
The base64 function decodes the user input and unserialize the result.
Summary : The goal is to find PHP gadgets in the PHP libraries of the application in order to read the
config.phpfile that contains the flag.
Kick-off gadget
First we need to find our kick-off gadget, this is the first gadget that will allow us to execute PHP code. For this we can look for objects that have one of the 2 magic methods : __wakeup and __destruct.
We find results, some of them are useless to us like the one present in the file ./app/vendor/guzzlehttp/psr7/src/FnStream.php :
|
|
and others are interesting like the one in the file ./app/vendor/guzzlehttp/psr7/src/Stream.php :
|
|
The code above call the function closeContent($this->size) on the attribute customMetadata of the class Stream. However, the function closeContent is never defined by any class.
What can we do now? We can use the magic method __call which is invoked when an undefined method is called. Indeed, we can search for objects that have the __call method.
Summary : The
Streamclass contains a magic method named__destructthat allows us to execute PHP code and start our chain of gadgets.
Second gadget
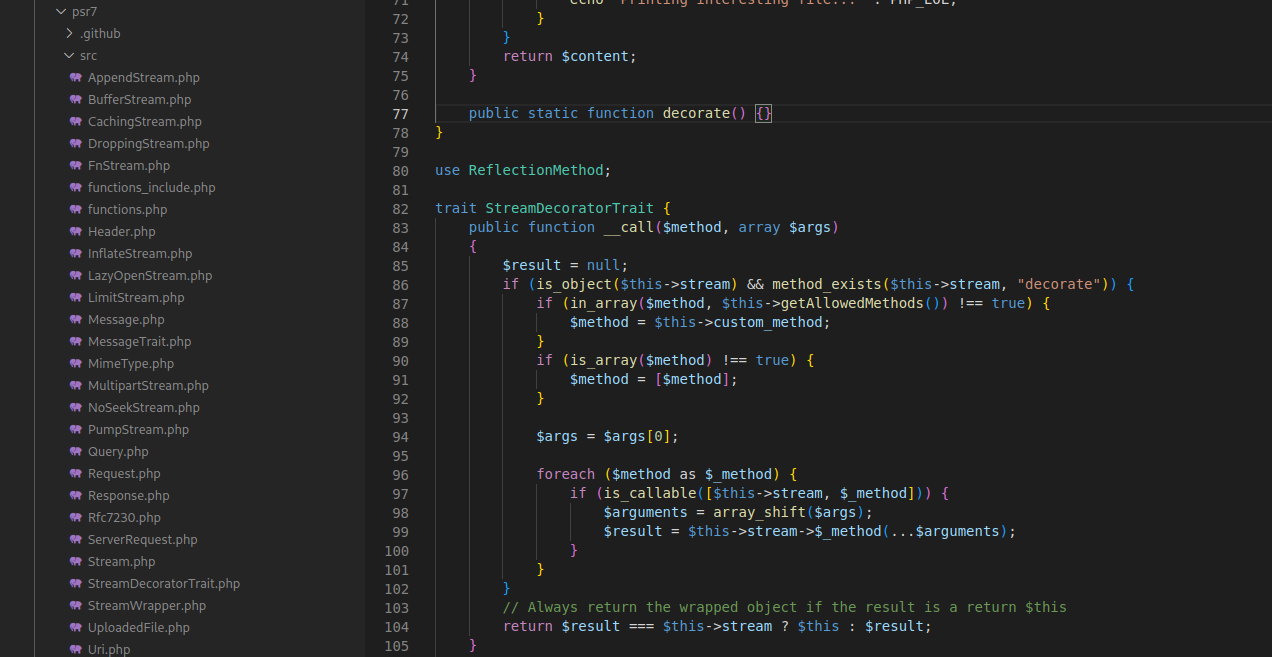
The class StreamDecoratorTrait in ./app/vendor/guzzlehttp/psr7/src/StreamDecoratorTrait.php has an interesting definition of the __call magic method.
|
|
- Parameters :
$methodis equals to the name of the missing method,closeContent.$argsis equals to the arguments of the missing method,$this->size(which is controlled by the attacker).
- Line 4 : The
streamattribute must be an object that has a method nameddecorate. - Line 5 : This condition is true because
closeContentis not ingetAllowedMethods(). So,$methodwill now be equals to$this->custom_method(which is controlled by the attacker). - Line 14 : The foreach loop will iterate over the list of methods and the list of arguments, then call the iterated method with its arguments on the instance in the
streamvariable.
Notice that StreamDecoratorTrait cannot be directly instantiated because it is a Trait (like Abstract class) and not a Class. For the final exploit, we will use the class CachingStream which inherits from StreamDecoratorTrait.
Summary: We can call any function with arguments on an object that has a method named
decorate.
Third gadget
After a quick search, we find a class named FnStream at ./app/vendor/guzzlehttp/psr7/src/FnStream.php which contains a method named decorate.
This class is very interesting because it has a method named getContents that allows us to read a PHP file. Remember, the goal is to read the config.php file.
|
|
display_contentmust be set totrue._fn_getContentsmust be set to/../../../../config(relative path from theFnStream.phpfile path).
So the $file variable will be equals to :
|
|
Summary: To get the flag, we need to call the
getContentsfunction on an instance ofFnStreamwith the attributesdisplay_contentset totrueand_fn_getContentsset to/../../../config.
Bypass FnStream protection
Unfortunately for us, the FnStream class has a magic method named __wakeup (invoked on unserialize) that unset all its class attributes.
|
|
So we can’t directly set display_content to true and _fn_getContents to /../../../../config because it will be unset at unserialization by the __wakeup method. However, the FnStream class has a method that allows us to set attribute.
|
|
So, if we call register("display_content", true) on an instance of FnStream, the attribute display_content of the instance will be set to true.
Notice that the _fn_getContents is inside forbidden_attributes, so we need to call the allow_attribute function first to remove it from the forbidden attributes :
|
|
Summary: To bypass the magic method named
__wakeupthat removes all the attributes of theFnStreamclass, we can use theregisterfunction to redefine them after the unserialization process.
Pack everything
To be able to test and debug my exploit more easily, I moved all the interesting classes, functions and attributes into a single file. Here is the result:
|
|
We now can try our exploit by visiting the URL : http://unserialkiller2.chall.malicecyber.com/?data=<base64_payload>
And get the flag :
|
|
This challenge was really interesting! A good note taking was necessary not to get lost on the way, then with a little time we manage to solve the challenge.