Follow The Rabbit - FCSC2023 Writeup
In this article, we will solve one of the hardest web challenges of the FCSC2023. Follow the Rabbit is a nginx server with a custom configuration.
Source code: SHA256(follow-the-rabbit-public.tar.gz) = 6d5af5b83e3c9d3d5bb556965440df80507406239e68ef94c03ba1482d99f411.
TL;DR
Abusing normalized URI and location to bypass regex and reach a specific location to obtain the flag.
Overview
The challenge is about bypassing an Nginx configuration to obtain the flag. The Nginx docker is defined in the following manner:
|
|
It should be noted that the current version of Nginx is 1.24.0, and not 1.23.3. Therefore, I attempted to find any security fixes that might exist between these versions, but nothing interesting comes up. You can view all the nginx versions on hg.nginx.org.
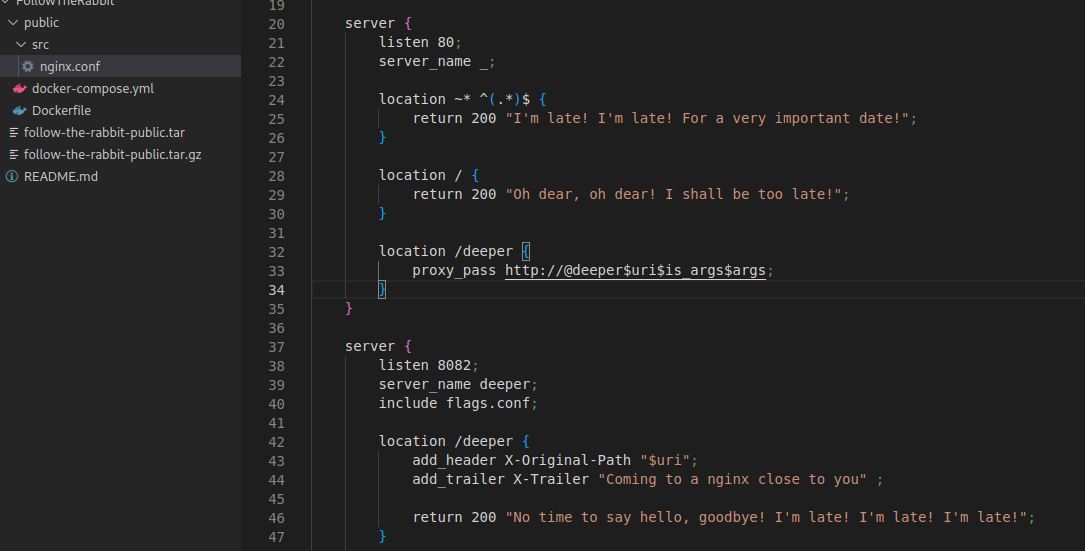
The Nginx configuration inside nginx.conf contains two server blocks but only the the port 80 is accessible (mapped on 8000).
|
|
To summarize:
- Exposed server -
0.0.0.0:80- Regex
~* ^(.*)$=>"I'm late! I'm late! For a very important date!" - Match
/=>"Oh dear, oh dear! I shall be too late!" - Match
/deeper=>proxy_pass http://@deeper$uri$is_args$args;
- Regex
- Internal server -
@deeper- Match
/deeper=>"No time to say hello, goodbye! I'm late! I'm late! I'm late!" - Match
/deepest=>"$flag"
- Match
This challenge involves two steps. The first one is to bypass the regex on the exposed server to reach the /deeper location. Consequently, our HTTP request will be fowarded to the internal server. The second steps involves directing the same HTTP request towards the /deepest location of the internal server.
location ~* ^(.*)$
On the nginx documentation about the location directive, we can see that the matching is done after URL decoding. So, if we insert a new line (%0A) in the path of our request, we can bypass the regex.
|
|
As you can see above, we reach the location / ! Now let’s try to reach the /deeper location.
proxy_pass
|
|
How it works ? The $uri variable is URL decode before sending the request to the internal server.
$uri: current URI in request, normalized (decoding the text encoded in the “%XX” form).
To do some debuging, we can edit the nginx configuration to send the proxy pass to a netcat server to see the HTTP request in plaintext.
|
|
We successfully forged a valid HTTP request by adding a fake header.
normalized URI
So, our last goal is to reach the /deepest location. To do that we need to use double URL encoding to match the /deeper location of the first server and the location /deepest of the second server.
- Server #1 location
/deeper:/deeper/%252E%252E%252Fdeepest($uri normalized) - Server #2 location
/deeper:/deeper/%2E%2E%2Fdeepest->/deeper/../deepest->/deepest(location normalized)
$uriandlocationarenormalized: The matching is performed against a normalized URI, after decoding the text encoded in the “%XX” form, resolving references to relative path components “.” and “..”, and possible compression of two or more adjacent slashes into a single slash.
|
|
We can now obtain the flag !!!
|
|